Architecture Design with the DNS-Broker
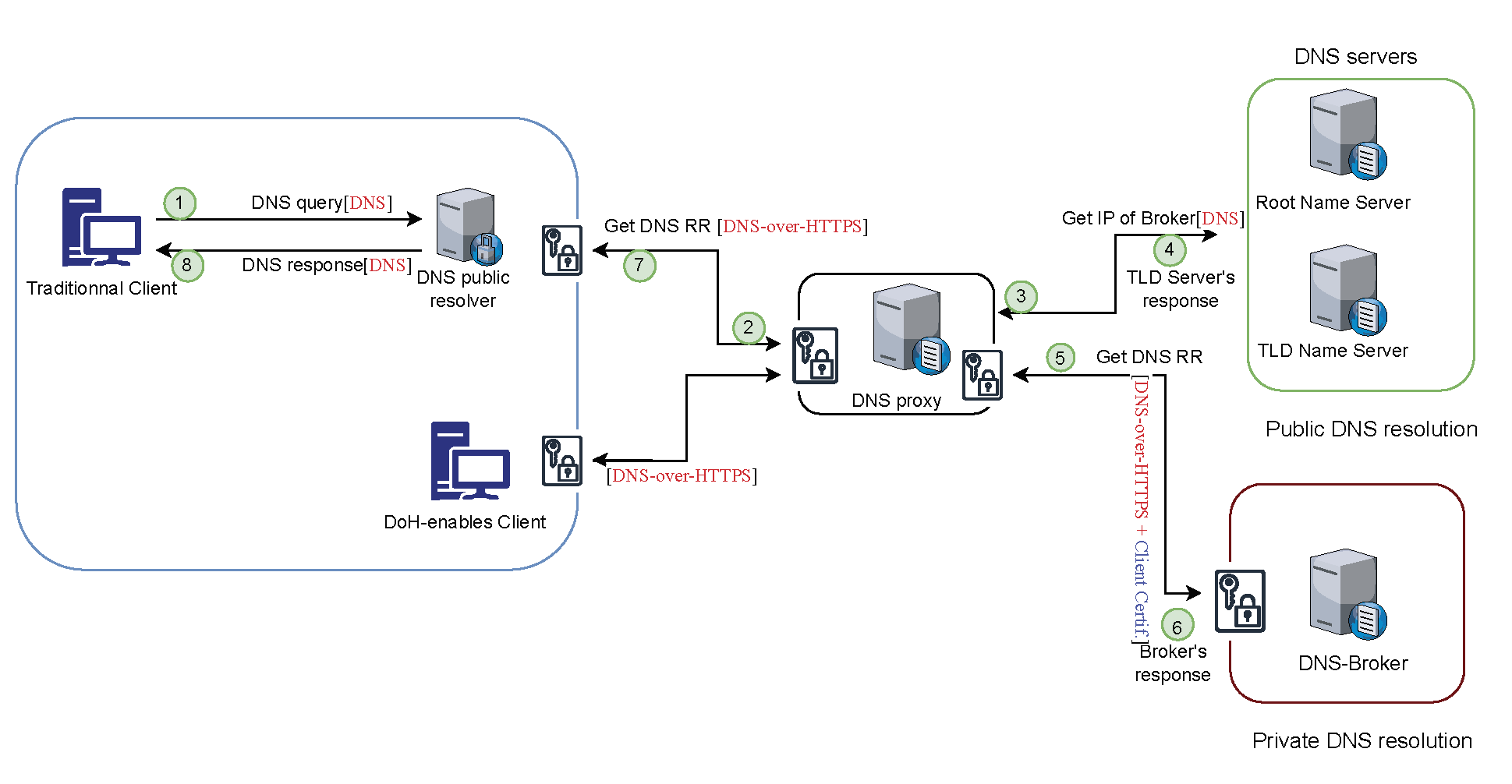
We have developed an architecture that introduces a new entity called the DNS-Broker. This new structure extends the capabilities of DoH (DNS over HTTPS) by segmenting access to the namespace. The proposed DNS-Broker introduces a distributed trust model, diverging from the traditional hierarchical approach. Our approach reduces the number of messages exchanged between the client and the DNS server during a resolution, which is pre-authorized through certificate-based validation.
PKI Infrastructure for Constrained Environments
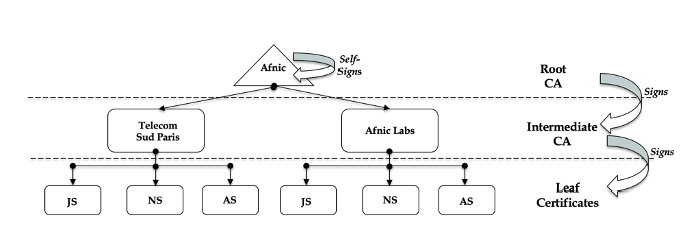
We demonstrated how DNS can provide PKI functionalities for IoT using DANE, supported by DNSSEC. Additionally, we designed and developed a tool to compress X.509 certificates, optimizing their size for constrained environments and ensuring their suitability for IoT protocols. Privacy Protection Mechanisms for Constrained Environments Protocols such as DoT, DoH, and DoQ provide a degree of security and privacy for DNS operations. We proposed a new format called efficient CBOR (e-CBOR) was introduced to make DNS messages more compact and flexible.
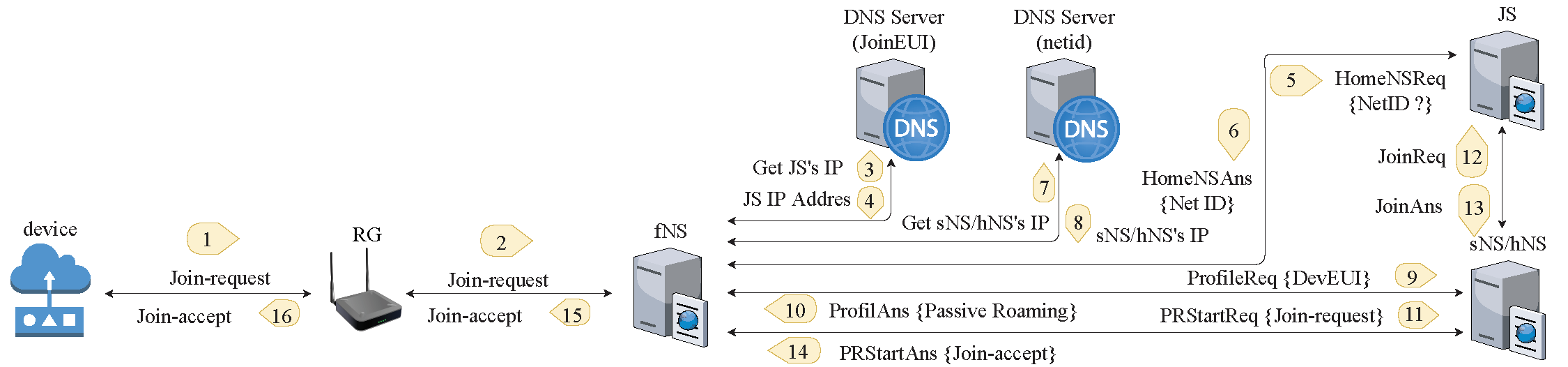
Design and Implementation of IoTRoam
We developed a flexible, scalable, and secure architecture for roaming in LoRaWAN networks, requiring minimal modifications to LoRaWAN or DNS protocols. The process of locating serving Network Servers (sNS) is simplified by leveraging DNS alongside a new DNS-Broker entity for private resolution using DoH. This innovation ensures scalability and security while showcasing DNS potential as a robust and reliable backbone for network operations.
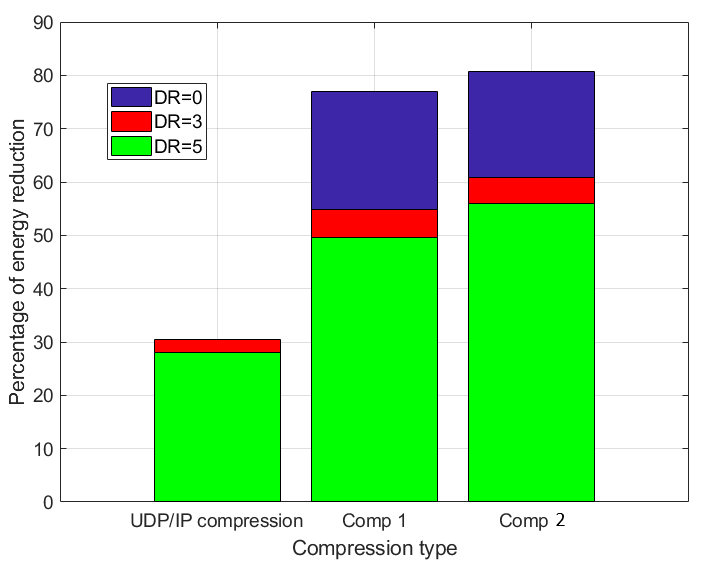
Evaluation of SCHC in LoRa Networks
We analyzed the impact of using SCHC (Static Context Header Compression and Fragmentation) on the energy consumption of LoRaWAN devices. SCHC compresses structured data (e.g., headers) and fragments long messages, enabling IPv6 packet transmission over LPWANs. Our evaluation demonstrated up to 81% reduction in device energy consumption and over four fold increase in network capacity for supported users.
Semantic Naming, Resolution, and Service Discovery Architecture for IoT Devices
We designed and implemented a metadata representation scheme for IoT devices within compact identifiers and DNS names to facilitate simple discovery using standard DNS servers. The scheme encodes an identifier as a bit sequence: a context and several semantic property fields specific to the context. The compact semantic DNS names enable querying and discovering IoT device properties, leveraging DNS as a foundational feature for semantic search and device discovery.